Best Construction Categories
Best Facilities Management Categories
Best Human Resources Categories
Best Legal Management Categories
Best Manufacturing Categories
Best Medical Categories
Best Property Management Categories
Get 1-on-1 advice in 15 minutes. It's free.

Josh P.

2026 Medical Software Trends: How Providers Can Prepare for Rising Costs and AI Adoption
Healthcare providers are entering 2026 in a climate of mounting financial and operational pressures. We recently conducted our annual Medical Software Trends survey of 400 U.S. physicians, and our findings reveal that cost escalation, workforce strain, and technology adoption are shaping priorities for the year ahead [1].
These forces are not isolated—they all combine to influence how practices plan, budget, and deliver care.
Here’s what we’ll cover in this report:
How medical software trends reflect the current market context
67% of respondents plan to increase their medical software spending in the next 12 months, and most say it’s due to price hikes.
49% of respondents reported that their expectations for AI have increased over the past year, but over a third are worried about over-reliance.
40% of practices with telehealth options are still using general-purpose video conferencing tools for appointments, putting themselves at risk.
Cybersecurity was identified as a leading software-related challenge by 27% of respondents.
What’s next?
How medical software trends reflect the current market context
One of the most pressing concerns for healthcare providers right now is the cost.
Nearly half of respondents (47%) identified high or rising expenses as their top challenge for the next 12 months. This trend reflects broader inflationary pressures and the growing complexity of healthcare delivery.
Rising costs are not just limited to supplies or facilities; technology investments are a major contributor. Practices must now weigh the benefits of advanced tools against the reality of tighter margins, making cost-control strategies essential.
Operational strain compounds these financial challenges.
Workforce burnout was cited by 34% of respondents as one of their top anticipated challenges of 2026, while 32% anticipate an increased patient load. These figures signal a system under stress, where staff shortages and surging demand will collide.
For many practices, this means finding ways to maintain quality care without overburdening clinicians—a balancing act that technology can help address if implemented thoughtfully.
However, technology spending is accelerating despite these pressures.
A striking 77% of practices expect software and technology investments to rise in the coming year. This surge underscores the industry’s recognition that digital tools are no longer optional—they are critical for efficiency, compliance, and patient engagement. However, the challenge lies in deploying these solutions effectively while managing costs and mitigating risks such as cybersecurity threats.
These trends set the stage for a pivotal year in healthcare technology. Rising costs demand smarter budgeting, while workforce strain calls for tools that reduce administrative burden. At the same time, increased technology investment signals opportunity—but also risk if practices fail to address governance, security, and usability.
The following sections explore the key findings from our survey and what they mean for providers preparing for 2026.
Key insight 1: Software price hikes burden healthcare
Healthcare practices are bracing for significant financial shifts in 2026, and software budgets are at the center of this change. Our survey reveals that two-thirds (67%) of respondents plan to increase their medical software spending in the next 12 months, with 8% anticipating a jump of more than 15%. This level of growth signals a strong commitment to technology, even as practices face broader cost challenges.
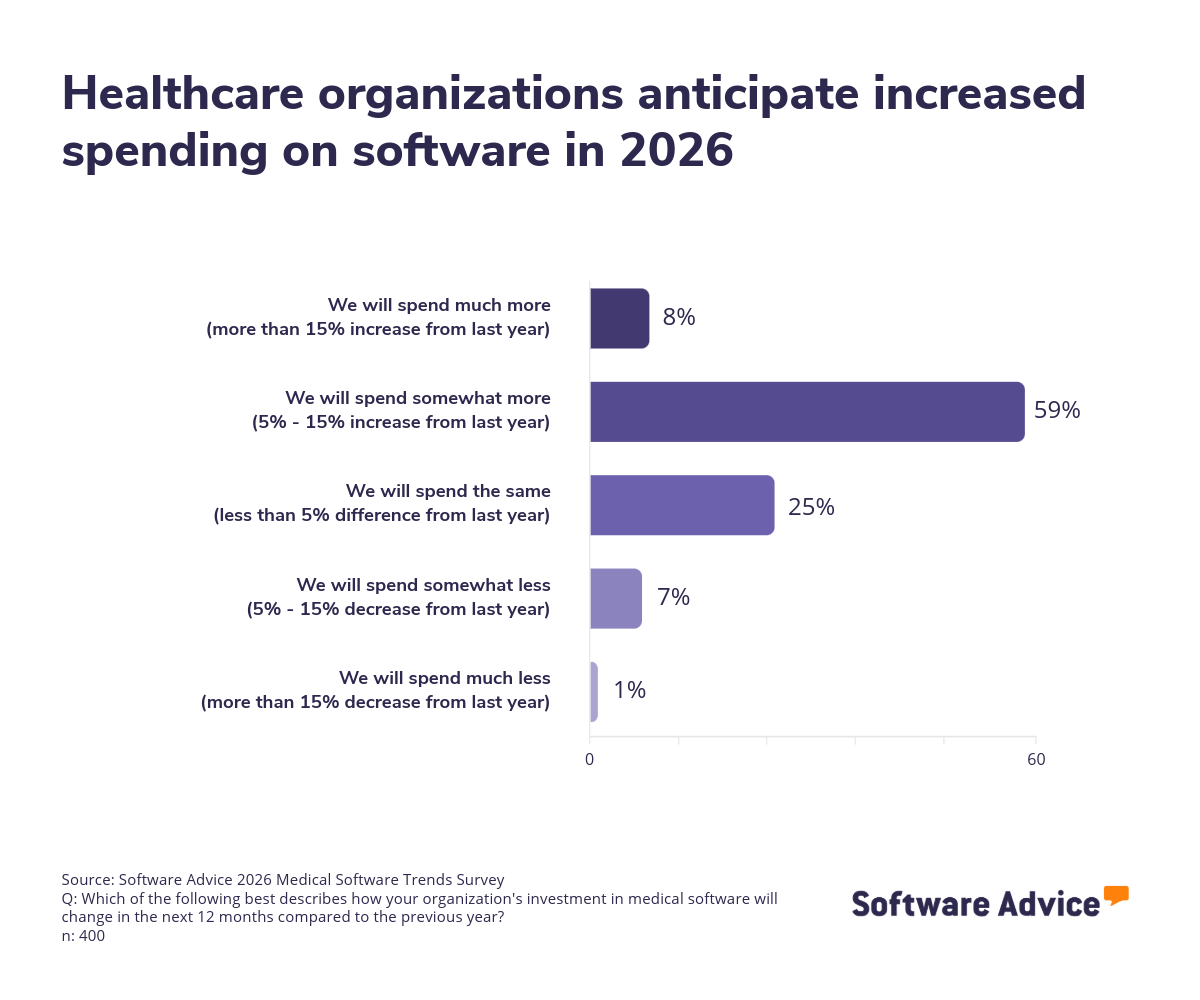
However, the primary driver behind these budget increases is not expanded functionality—it’s rising software prices: 28% of respondents who are increasing spending this year cited price hikes as the top reason for spending more, outpacing motivations such as adding new features or adopting entirely new systems. This indicates that inflationary pressures in the software market are forcing practices to spend more just to maintain current capabilities.
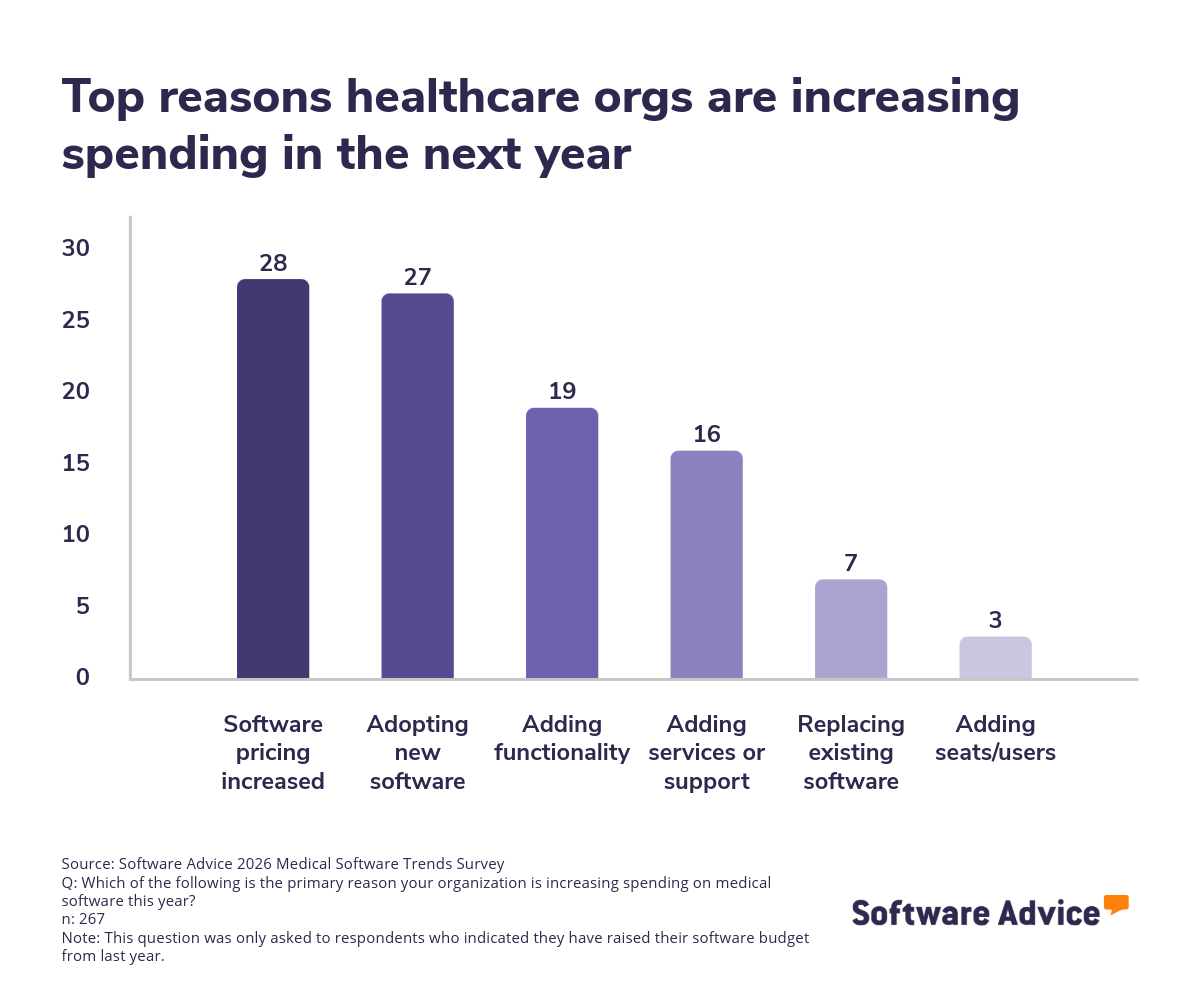
This finding suggests that practices are being forced to allocate more funds simply to maintain existing capabilities.
It’s noteworthy that costs are rising for almost every aspect of running a practice. Our survey found that all costs, except for staff training, are expected to rise by more than half of the professionals surveyed in the coming year. That includes things like facility expenses, medical supplies and equipment, maintenance costs, insurance and legal fees, regulatory and compliance costs, among others.
And yet, technology investments lead the pack among expected cost increases—77% of practices expect software and technology expenses to rise in the coming year.
Inflation is certainly one big factor causing these price hikes, but there are other, more complex elements at play here. For example, the features of healthcare software are growing more and more complex thanks to things like increased security demands and artificial intelligence (AI) integrations. Add to that the recent supply chain complications and costs associated with tariffs, and you get a perfect storm.
While this trend underscores the growing reliance on digital tools for clinical workflows, patient engagement, and compliance, it also raises questions about sustainability—how will practices balance the need for innovation with the imperative to control costs?
Recommendations
Rising software costs are unavoidable, but overspending is not. Practices should take proactive steps to manage this trend:
Negotiate multi-year contracts to lock in pricing and avoid annual increases.
Evaluate bundled solutions that consolidate functionality and reduce vendor complexity.
Prioritize ROI-driven features—focus on tools that directly improve efficiency or revenue rather than chasing “nice-to-have” capabilities.
These actions can help healthcare organizations maintain financial stability while continuing to invest in technology that supports patient care and operational resilience.
Key insight 2: Practices should weigh AI benefits against safety gaps
Artificial intelligence is moving from concept to reality in healthcare. Nearly half (49%) of respondents reported that their expectations for AI have increased over the past year, indicating growing confidence in its potential to transform clinical and administrative workflows.
This optimism is carried out in adoption patterns, too—among the third of practices currently using AI tools, 42% leverage natural language processing (NLP) for documentation, 36% use large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT, and 31% employ AI-powered clinical decision support systems (CDSS).
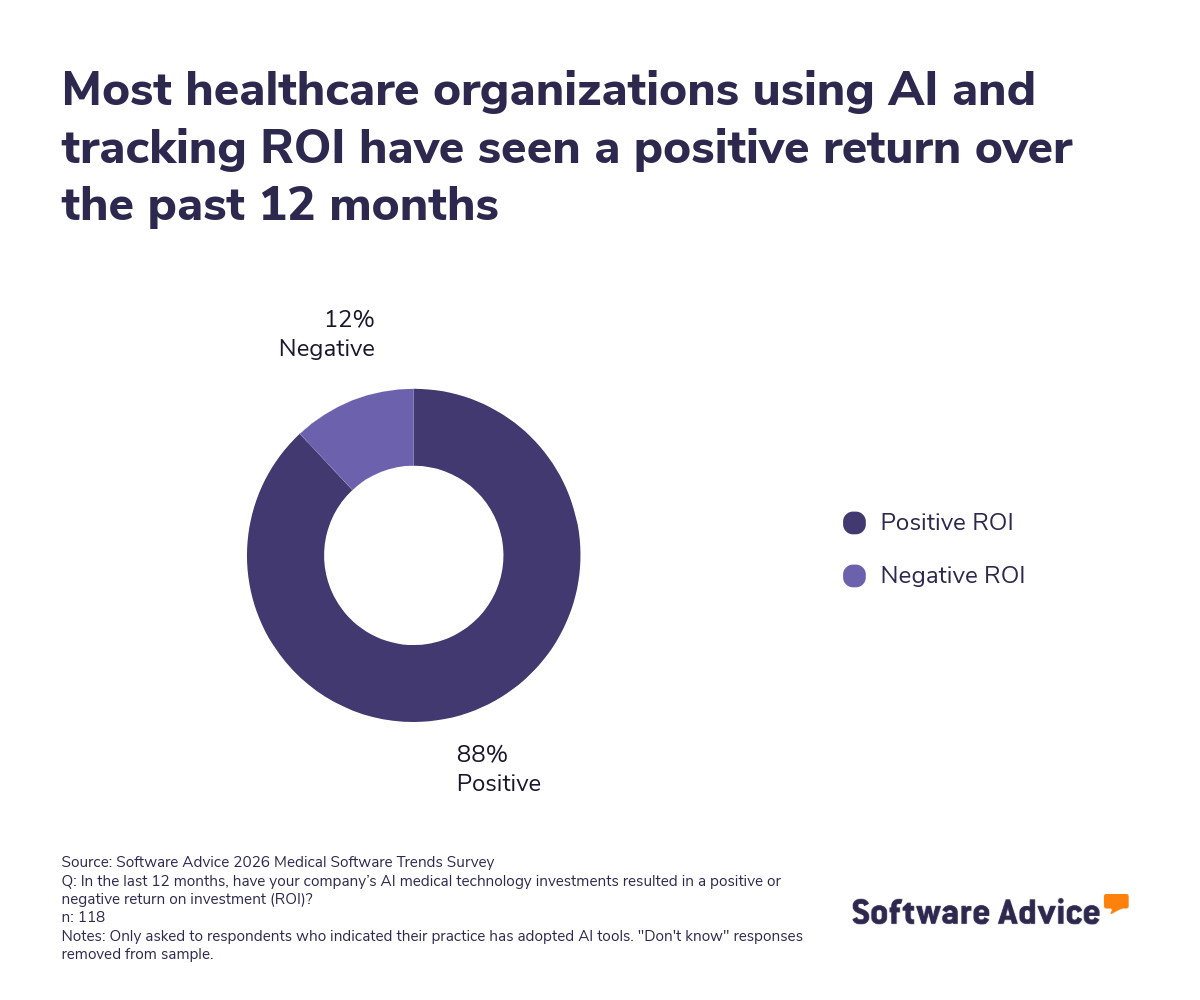
However, enthusiasm comes with caution. One of the top challenges of leveraging AI features in healthcare cited by all respondents is overreliance on AI recommendations (37%), followed by concerns about data quality, privacy, and algorithm transparency. These issues highlight the tension between innovation and risk management. While AI promises efficiency gains, it also introduces new vulnerabilities if governance and training are overlooked.
This tension is especially pronounced in clinical settings, where AI-generated recommendations may be perceived as authoritative—even when they lack sufficient context or validation. The survey shows that while 33% of practices use AI tools, only 57% of those report a positive return on investment (ROI). This suggests a growing reliance on AI despite moderate evidence of consistent value delivery.
The gap between rising expectations and measured outcomes may reflect a broader challenge: Practices are adopting AI faster than they’re building the internal capabilities to manage it.
Without clear protocols for interpreting AI outputs, clinicians risk deferring judgment to systems that may not account for patient-specific nuances or evolving clinical standards.
Recommendations
AI adoption is accelerating, but success depends on responsible implementation. Healthcare providers should:
Develop governance frameworks to define how AI recommendations are validated before clinical use.
Invest in staff training to build confidence and reduce reliance on automated outputs.
Audit data quality and security to ensure AI systems operate on accurate, compliant information.
These steps will help practices harness AI’s benefits while mitigating risks that could compromise patient safety or regulatory compliance.
Key insight 3: The telemedicine tools you use matter
Virtual care is now a permanent part of healthcare delivery, but the tools used to deliver it are under increasing scrutiny.
On average, 17% of monthly appointments are conducted virtually, reflecting sustained demand for remote services. However, 40% of practices rely on general-purpose platforms like Zoom or Microsoft Teams for telehealth—tools originally designed for business meetings, not clinical care.
These platforms were temporarily approved for medical use during the COVID-19 emergency, but that discretion expired in 2023. Today, continued use of these tools without proper configuration or licensing may expose providers to HIPAA violations and legal risk.
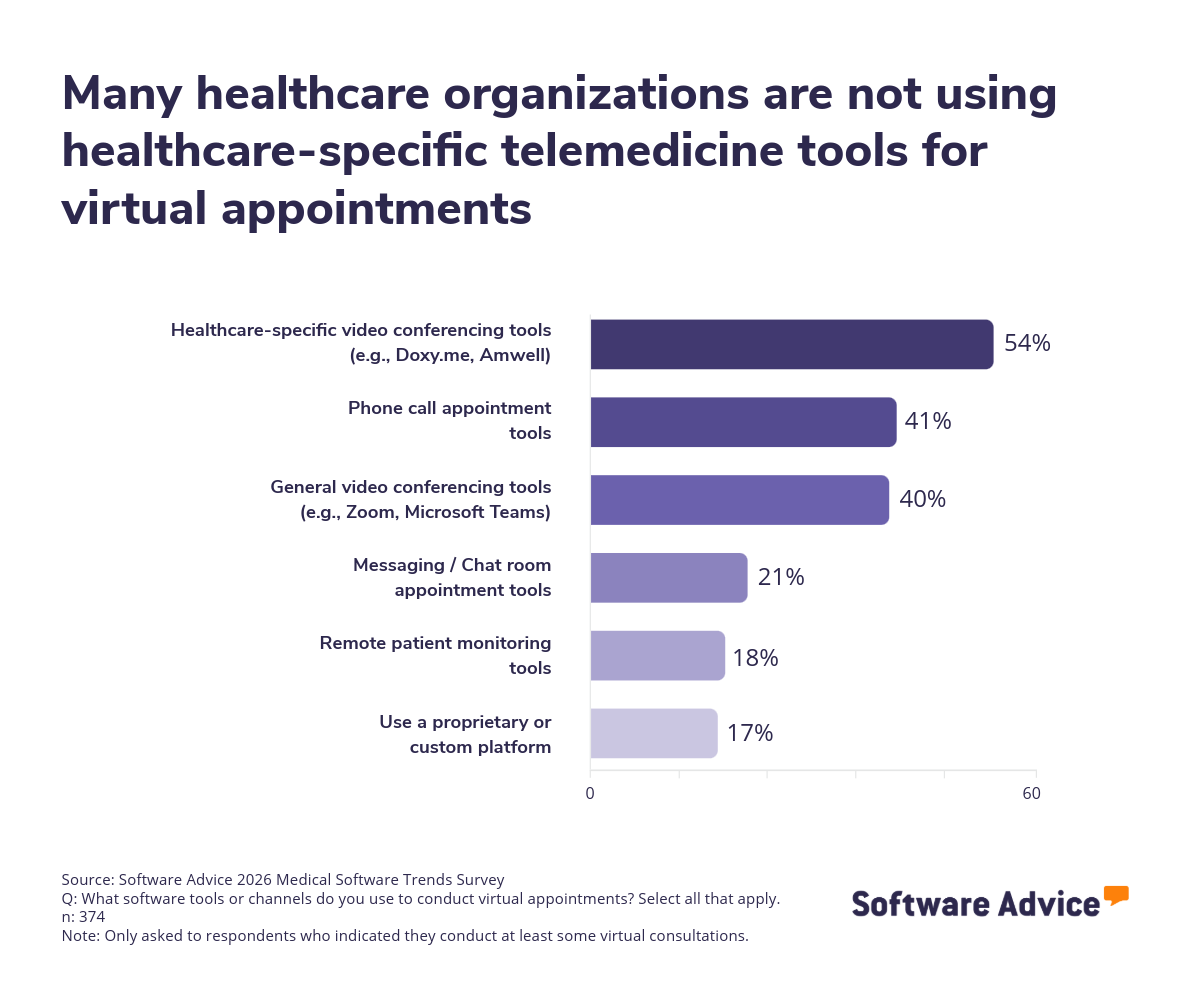
General video tools often lack built-in safeguards for handling protected health information (PHI), such as automatic encryption, access controls, and audit trails. Without a signed Business Associate Agreement (BAA) and proper configuration, using these platforms for telehealth may violate HIPAA’s Privacy and Security Rules. Even when BAAs are in place, compliance depends on how the software is deployed and used—not just the tool itself.
Clinical limitations also become an issue for these practices. General-purpose platforms typically don’t integrate with electronic health record (EHR) systems, which can lead to fragmented documentation, missed data, and increased administrative burden.
Recommendations
To reduce risk and improve care quality, healthcare providers should:
Transition to HIPAA-compliant telehealth platforms that offer native EHR integration, secure data handling, and signed BAAs.
Review legal obligations post-COVID and ensure all virtual care tools meet current HIPAA standards.
Audit workflows to identify where general-purpose tools may be causing data gaps or compliance risks.
These steps can help practices deliver virtual care that’s not only convenient—but also secure, compliant, and clinically sound.
Key insight 4: Many practices aren’t prepared for HIPAA revisions
Regulatory compliance and cybersecurity remain top of mind as proposed HIPAA revisions are currently being debated.
Our survey shows that 29% of practices need significant improvement in data protection and network security to align with these proposed revisions, while 28% cite vulnerability management as a critical gap. These findings align with broader concerns: cybersecurity was identified as a leading software-related challenge by 27% of respondents.
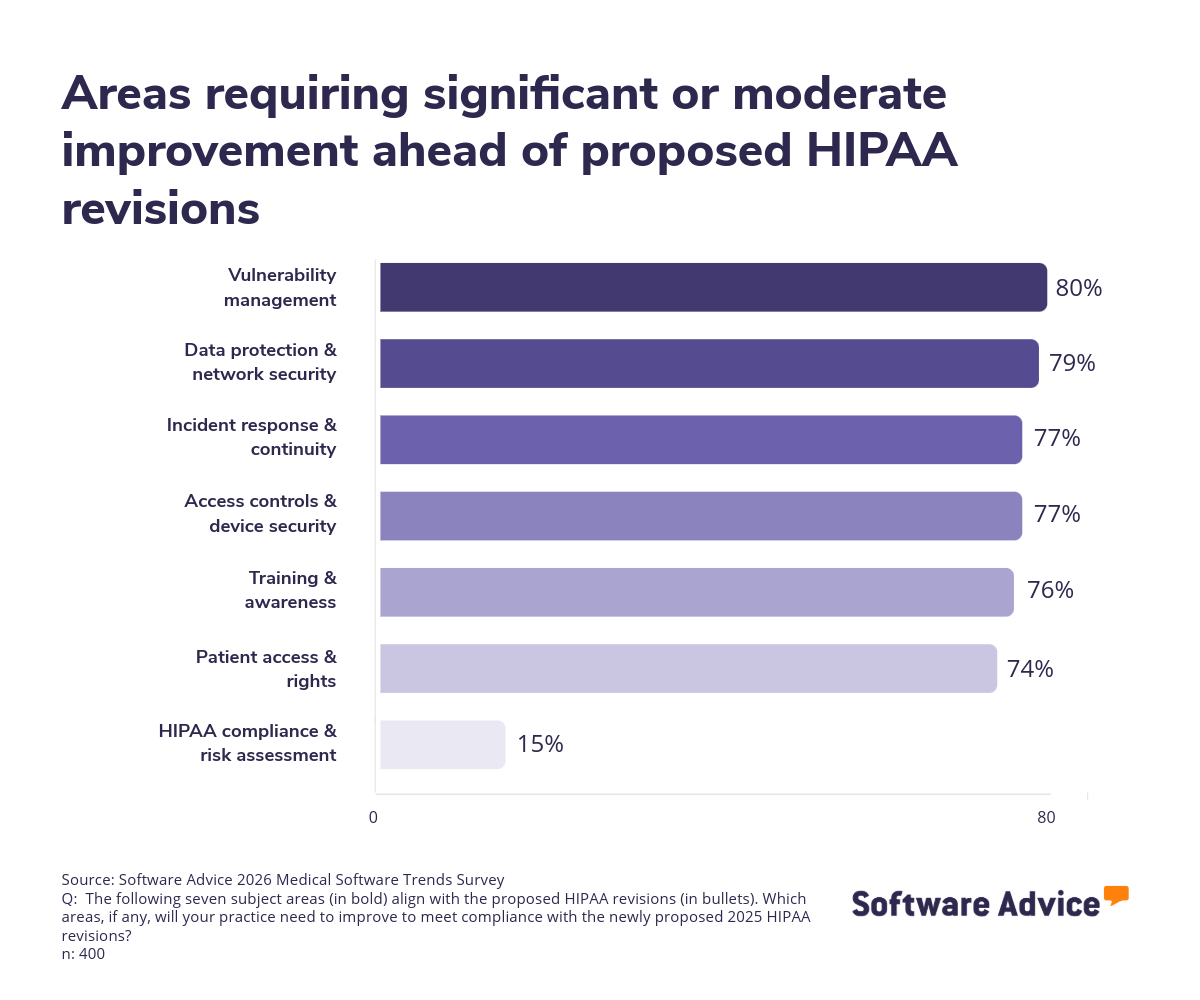
The stakes are high. Compliance failures can result in financial penalties and reputational damage, while security breaches jeopardize patient trust. Practices must address these gaps proactively, especially as technology adoption expands attack surfaces.
Recommendations
Compliance and security are non-negotiable. Providers should:
Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) and encryption protocols for all patient data.
Conduct regular vulnerability scans and penetration testing to identify and remediate risks.
Update HIPAA training programs to ensure staff understand new requirements and best practices.
By prioritizing these measures, practices can safeguard patient information and maintain regulatory alignment as digital transformation accelerates.
What’s next?
The year ahead presents both challenges and opportunities for healthcare providers. Rising software costs, workforce strain, and compliance requirements demand careful planning, while accelerating AI adoption and virtual care expansion offer pathways to greater efficiency and improved patient outcomes.
Success will hinge on making informed technology decisions—prioritizing solutions that deliver measurable value, enhance security, and support sustainable growth.
To prepare for 2026, healthcare practices should focus on four critical actions:
Budget strategically: Negotiate multi-year software contracts and explore cost-control measures to offset price hikes.
Prioritize AI readiness: Train staff and implement governance frameworks to avoid overreliance and ensure safe AI use.
Upgrade virtual care platforms: Transition from generic video tools to purpose-built telehealth solutions for better integration and compliance.
Strengthen cybersecurity and HIPAA compliance: Focus on encryption, multi-factor authentication, and vulnerability management.
Remember, healthcare leaders don’t have to navigate these decisions alone. Software Advice’s team of expert advisors can help you research, compare, and select medical practice software tailored to your organization’s needs. Whether you’re evaluating telehealth platforms, exploring AI-driven tools, or seeking compliance-ready solutions, our advisors provide personalized guidance at no cost when you’re ready to take that step.